Compare MotoSuiveur®
MotoSuiveur® vs. the competition
Why secure your hoist with MotoSuiveur®? Discover how it compares to other solutions on the market.
Basic Open Chain hoist
en anglais
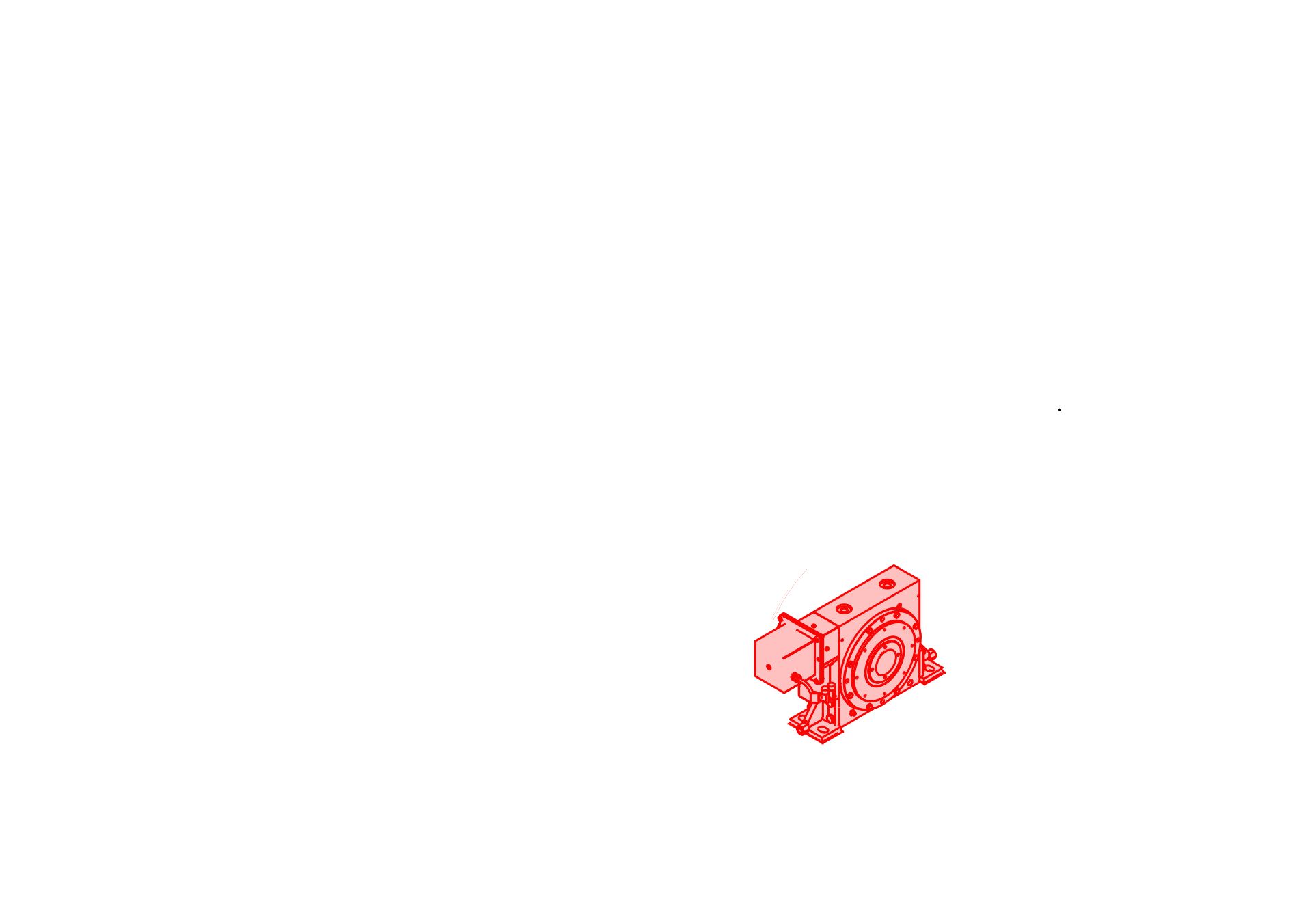
MotoSuiveur®-secured hoist
en anglais
Safety Design Measures
Very Limited Safeguards
Motor service brake
Inherently Safe Design
Positive Mechanical Action at the Drum, Safety Decoupled from Operation
Benefits
✓ ✓ ✓ Instant arrest,
Shortest arrest distance
Shortest arrest distance
✓ ✓ ✓ Solves human error
✓ ✓ ✓ Overload protection
✓ ✓ ✓ Safe load recovery
✓ ✓ ✓ Compact, Sealed
✓ ✓ ✓ Retrofittable
✓ ✓ ✓ No wear parts
Drawbacks
Défaillance électrique
Load drop
20 - 50 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
Défaillance mécanique
Load drop
20 - 50 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
Accrochage de charge
Load drop
✓ Torque limiter
Mouflage
Load drop
✓ Torque limiter
Survitesse
✕
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Glissement de charge
✕
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Détection de rupture
✕
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Détection de surcharge
✕
✓ Intrinsic passive function, 0 delay
Fiabilité mécanique
Possible failure, a brake may remain open
✓ Impossible failure (positive action)
Couple de freinage
Depends on many factors and the environment
Stable, impervious to the environment
Descente
Significant risks
✓ Simple and safe
Opération de récupération
✕
✓ Always possible, Remote operation
Tests
No (Basic verifications)
✓ Simple and safe
Pièces d'usure
Linings, discs
✓ No wear parts
Dimensions et masse
Prix d'achat
Coût total de possession
Open chain hoist with safety brake
en anglais

MotoSuiveur®-secured hoist
en anglais
Safety Design Measures
Safeguards
Mechanical load brakes, Redundant braking systems, Overload protection devices, Limit switches
Inherently Safe Design
Positive Mechanical Action at the Drum, Safety Decoupled from Operation
Benefits
✓ ✓ ✓ Relatively compact
✓ ✓ ✓ Retrofittable (under conditions)
✓ ✓ ✓ Instant arrest,
Shortest arrest distance
Shortest arrest distance
✓ ✓ ✓ Solves human error
✓ ✓ ✓ Overload protection
✓ ✓ ✓ Safe load recovery
✓ ✓ ✓ Compact, Sealed
✓ ✓ ✓ Retrofittable
✓ ✓ ✓ No wear parts
Drawbacks
✕ Uncertain state of the brake, may not close properly
✕ Highly susceptible to wear and the environment
✕ May create severe overstress, fatigue
✕ Safety depends on complex electronics, maintenance
✕ ~2 meters low-approach zone
Défaillance électrique
150 - 300 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
20 - 50 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
Défaillance mécanique
500 - 2000 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
20 - 50 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
Accrochage de charge
Load Cell and electronic detection of the overload
✓ Torque limiter
Mouflage
Switch overtravel for Upper-Limit Switch
✓ Torque limiter
Survitesse
Electronic measurement and detection
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Glissement de charge
Electronic measurement and detection
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Détection de rupture
~ Numerous encoders,
Complex electronics (SIL, PL),
Demanding maintenance
Complex electronics (SIL, PL),
Demanding maintenance
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Détection de surcharge
~ Electronic system, reaction time
✓ Intrinsic passive function, 0 delay
Fiabilité mécanique
Possible failure, a brake may remain open
✓ Impossible failure (positive action)
Couple de freinage
Depends on many factors and the environment
Stable, impervious to the environment
Descente
Complex operation, significant risks
✓ Simple and safe
Opération de récupération
Impossible in case of breakage
✓ Always possible, Remote operation
Tests
Difficult to ensure the proper functioning of securities
✓ Simple and safe
Pièces d'usure
Linings, discs
✓ No wear parts
Dimensions et masse
Prix d'achat
Coût total de possession
Closed hoist or redundant chain
en anglais

MotoSuiveur®-secured hoist
en anglais
Safety Design Measures
Safeguards
Partially Inherently Safe Design
Dual load paths, Redundant braking systems, Multiple limit switches and overload detection
Inherently Safe Design
Positive Mechanical Action at the Drum, Safety Decoupled from Operation
Benefits
✓ ✓ ✓ Single failure proof
✓ ✓ ✓ Short arrest distances thanks to important inertia
✓ ✓ ✓ Load recovery possible
✓ ✓ ✓ Instant arrest,
Shortest arrest distance
Shortest arrest distance
✓ ✓ ✓ Solves human error
✓ ✓ ✓ Overload protection
✓ ✓ ✓ Safe load recovery
✓ ✓ ✓ Compact, Sealed
✓ ✓ ✓ Retrofittable
✓ ✓ ✓ No wear parts
Drawbacks
✕ Common failure modes of 2 identical transmissions
✕ Congestion, weight
✕ Not retrofittable
✕ Price
Défaillance électrique
100 - 200 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
20 - 50 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
Défaillance mécanique
30 - 60 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
20 - 50 mm
load arrest distance
load arrest distance
Accrochage de charge
Load Cell and electronic detection of the overload
✓ Torque limiter
Mouflage
Switch overtravel for Upper-Limit Switch
✓ Torque limiter
Survitesse
~ Electronic measurement and detection
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Glissement de charge
~ Electronic measurement and detection
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Détection de rupture
~ Numerous encoders,
Complex electronics (SIL, PL),
Demanding maintenance
Complex electronics (SIL, PL),
Demanding maintenance
✓ Intrinsic passive function
Détection de surcharge
~ Electronic system, reaction time
✓ Intrinsic passive function, 0 delay
Fiabilité mécanique
Possible failure, a brake may remain open
✓ Mitigated by brake redundancy
✓ Mitigated by brake redundancy
✓ Impossible failure (positive action)
Couple de freinage
Depends on many factors and the environment
Stable, impervious to the environment
Descente
✕ Complex operation, significant risks
✓ Simple and safe
Opération de récupération
✓ Always possible
✓ Always possible, Remote operation
Tests
Difficult to ensure the proper functioning of securities
✓ Simple and safe
Pièces d'usure
Linings, discs
✓ No wear parts
Dimensions et masse
Prix d'achat
Coût total de possession